In an increasingly digital world where seamless information transfer and accessibility are paramount, QR code generators have become essential tools for businesses, organizations, and individuals alike. The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator instant-use/qr-code-generator represents a sophisticated yet user-friendly implementation of QR code technology that exemplifies modern web-based utility design. This comprehensive analysis examines every aspect of this tool, from its user interface and functionality to its underlying technical architecture and practical applications.
This tool stands out in the crowded QR code generator market by offering a combination of simplicity, customization options, and professional-grade output without requiring user registration or payment. The service transforms any text or URL into a visually appealing, scannable QR code while providing color customization options and multiple download formats. This analysis will explore the technical foundations, backend architecture, user experience design, and practical applications that make this tool valuable for diverse use cases.
QR Code Technology
Quick Response (QR) codes, invented by Denso Wave in 1994 for tracking automotive parts, have evolved into one of the most versatile data encoding systems in modern digital communication. Unlike traditional barcodes that store information horizontally, QR codes utilize a two-dimensional matrix that can store significantly more data in a compact format.
The fundamental principle behind QR codes lies in their ability to encode various types of information including text, URLs, contact information, Wi-Fi credentials, and more, into a machine-readable format. Each QR code consists of black squares arranged in a square grid on a white background, with specific patterns that enable rapid recognition and decoding by QR scanners and smartphone cameras.
The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator leverages this established technology while adding modern conveniences such as color customization, instant generation, and multiple export options. The tool’s significance extends beyond mere convenience; it represents a bridge between complex encoding algorithms and practical everyday applications.
Tool Overview and Core Features
Primary Functionality
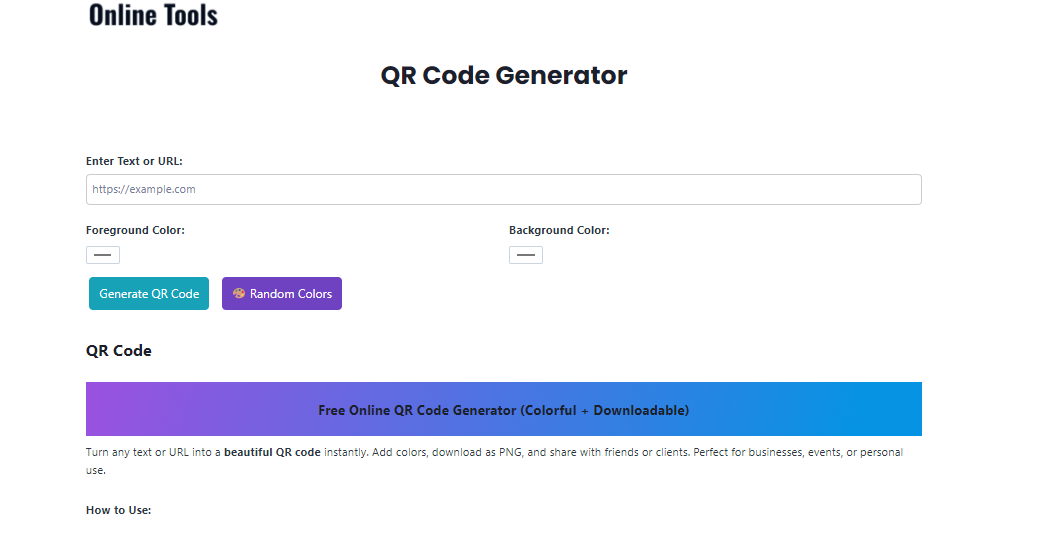
The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator operates as a browser-based application that converts text input into QR codes without requiring software installation or user registration. The tool’s core functionality encompasses several key features:
Instant QR Code Generation: Users can input any text string or URL and receive an immediately generated QR code. The generation process occurs in real-time, with codes appearing within milliseconds of input completion.
Color Customization: Unlike basic QR generators that produce only black-and-white codes, this tool offers comprehensive color customization. Users can modify both the foreground pattern color and background color, enabling brand alignment and aesthetic preferences.
Transparent Background Support: The tool supports transparent backgrounds, a feature particularly valuable for graphic designers and marketers who need to overlay QR codes on various backgrounds without white boxing.
Multiple Format Support: Generated QR codes can be downloaded in PNG format, ensuring compatibility with virtually all digital and print applications.
No Registration Required: The tool operates without requiring user accounts, email verification, or personal information, prioritizing user privacy and convenience.
User Interface Design
The interface exemplifies modern web design principles with a clean, intuitive layout that guides users through the QR generation process. The design philosophy emphasizes functionality over ornamentation, with every interface element serving a specific purpose in the workflow.
The main interface consists of several key areas:
Input Section: A clearly labeled text field where users enter their desired text or URL. The field accepts unlimited character input, though practical QR code limitations apply based on the chosen error correction level.
Customization Panel: Color selection tools that allow users to choose both foreground and background colors through either color pickers or hex code input. This section includes preview functionality that updates the QR code appearance in real-time.
Generation Area: A dedicated space where the QR code appears immediately upon input completion. The generated code displays at sufficient resolution for both digital viewing and print applications.
Download Section: Simple, prominent download buttons that enable immediate file saving without additional steps or redirects.
Technical Architecture and Backend Implementation
Frontend Technologies
The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator utilizes modern web technologies to deliver a responsive, cross-platform experience. The frontend implementation relies heavily on JavaScript for real-time QR code generation and user interaction handling.
HTML5 Structure: The application employs semantic HTML5 elements that provide accessibility benefits and search engine optimization. The structure follows progressive enhancement principles, ensuring basic functionality remains available even with limited browser capabilities.
CSS3 Styling: Advanced CSS3 features enable the tool’s responsive design and smooth user interactions. The styling system uses flexible layouts that adapt to various screen sizes and device orientations.
JavaScript Core: The primary logic executes in client-side JavaScript, enabling immediate QR code generation without server round-trips. This approach reduces server load while providing instantaneous user feedback.
QR Code Generation Algorithm
The technical foundation of any QR code generator lies in its encoding algorithm. While the specific implementation details of the Online-Tools.io generator are proprietary, the underlying principles follow established QR code standards defined in ISO/IEC 18004.
Data Analysis and Mode Selection: The algorithm begins by analyzing the input data to determine the most efficient encoding mode. QR codes support several encoding modes including numeric, alphanumeric, byte, and Kanji modes, each optimized for specific character sets.
Error Correction Level Determination: QR codes incorporate Reed-Solomon error correction, which enables partial data recovery even when portions of the code are damaged or obscured. The algorithm selects an appropriate error correction level based on the data complexity and intended use case.
Version Selection: QR codes come in 40 different versions, ranging from 21×21 modules (Version 1) to 177×177 modules (Version 40). The algorithm automatically selects the smallest version capable of containing the encoded data plus error correction information.
Data Encoding: The actual data encoding process converts the input string into a binary format suitable for QR code representation. This involves applying the selected encoding mode and adding necessary formatting information.
Error Correction Code Generation: Using Reed-Solomon algorithms, the system generates error correction codewords that enable data recovery. The specific implementation uses finite field mathematics to create redundant information mathematically related to the original data.
Module Placement: The final step involves arranging the encoded data and error correction codes within the QR code matrix, following specific patterns that include finder patterns, separator patterns, timing patterns, and alignment patterns.
Backend Infrastructure
While the primary QR generation occurs client-side, the Online-Tools.io platform requires sophisticated backend infrastructure to support the service.
Content Delivery Network (CDN): Static assets including JavaScript libraries, CSS files, and images are distributed through a CDN to ensure fast loading times globally. This infrastructure reduces latency and improves user experience across different geographical locations.
Server Architecture: The backend likely employs a microservices architecture to handle various aspects of the service including user analytics, performance monitoring, and content delivery. Modern web applications typically use Node.js or similar technologies for backend services.
Database Systems: While the QR generator itself may not require persistent storage, the platform maintains databases for analytics, performance metrics, and service monitoring. These systems likely use both relational and NoSQL databases depending on the specific data requirements.
API Management: The service may provide API endpoints for programmatic access, requiring authentication, rate limiting, and request management systems.
Reed-Solomon Error Correction Deep Dive
Theoretical Foundation
The reliability of QR codes under adverse conditions stems from their implementation of Reed-Solomon error correction, a mathematical approach to data redundancy developed in 1960. This system enables QR codes to remain functional even when up to 30% of the code area is damaged or obscured.
Mathematical Basis: Reed-Solomon codes operate in finite fields (Galois fields), mathematical structures that enable efficient computation of error correction polynomials. The algorithm treats data as coefficients of polynomials and uses mathematical operations to generate redundant information.
Error Detection and Correction: The system can detect errors up to the number of check symbols added to the original data. For correction, it can fix up to half the number of check symbols. For example, if 10 check symbols are added, the system can detect 10 errors or correct 5 errors.
Burst Error Handling: Unlike simple parity systems that handle individual bit errors, Reed-Solomon correction excels at handling burst errors where multiple consecutive bits are corrupted. This characteristic makes it ideal for QR codes, which may suffer damage in localized areas.
Implementation in QR Codes
QR codes implement Reed-Solomon correction at four different levels, each offering different balances between data capacity and error resilience:
Level L (Low): Recovers approximately 7% of codewords, suitable for clean environments where damage is unlikely.
Level M (Medium): Recovers approximately 15% of codewords, appropriate for most general-purpose applications.
Level Q (Quartile): Recovers approximately 25% of codewords, ideal for applications where partial obscuration is possible.
Level H (High): Recovers approximately 30% of codewords, optimal for harsh environments or when maximum reliability is required.
The Online-Tools.io generator likely implements adaptive error correction level selection based on the input data characteristics and intended use case, though users may not directly control this selection.
Data Encoding Methods and Optimization
Encoding Mode Analysis
QR codes support multiple encoding modes, each optimized for specific character sets and data types. The Online-Tools.io generator must analyze input data to select the most efficient encoding method.
Numeric Mode: Optimized for strings containing only digits (0-9), this mode provides the highest data density. Every three digits are encoded in 10 bits, making it ideal for identification numbers, phone numbers, and purely numeric data.
Alphanumeric Mode: Supports digits, uppercase letters, space, and several symbols ($ % * + – . / :). Two characters are encoded in 11 bits, making it suitable for URLs and basic text that fits the limited character set.
Byte Mode: Accommodates any 8-bit character, including lowercase letters, extended ASCII, and binary data. Each character requires 8 bits, making it the most versatile but least efficient mode for basic text.
Kanji Mode: Specifically designed for Japanese Kanji characters, encoding each character in 13 bits. This mode is rarely used in international applications but demonstrates QR codes’ multilingual capabilities.
Mixed Mode: Advanced QR generators can switch between modes within a single code to optimize data density. This technique requires sophisticated analysis to determine optimal mode boundaries.
Data Compression and Optimization
The Online-Tools.io generator likely implements several optimization strategies to maximize data efficiency:
Automatic Mode Selection: The algorithm analyzes input data to determine which encoding mode or combination of modes produces the smallest QR code version.
Character Set Analysis: By examining the complete input string before encoding, the system can make informed decisions about mode switching points and optimal encoding strategies.
Structured Append: For extremely large data sets, QR codes can be split across multiple codes using structured append mode. While not commonly needed for typical web applications, this feature enables encoding of substantial amounts of information.
Backend Architecture Analysis
Modern Web Application Stack
The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator represents a modern web application that likely employs several industry-standard technologies and architectural patterns.
Frontend Framework: The user interface likely utilizes a modern JavaScript framework or vanilla JavaScript with modern ECMAScript features. The real-time QR generation suggests event-driven programming with immediate DOM updates.
Build Process: Modern web applications employ build tools for code optimization, asset bundling, and deployment automation. The service likely uses tools like Webpack, Rollup, or similar bundlers to optimize client-side code.
Progressive Web Application Features: The tool may implement PWA features such as service workers for offline functionality and manifest files for app-like behavior on mobile devices.
Server-Side Infrastructure
Load Balancing: To handle traffic distribution and ensure high availability, the service likely employs load balancing across multiple server instances. This infrastructure supports global accessibility and prevents single points of failure.
Caching Strategies: Various caching layers optimize performance:
- Browser caching for static assets
- CDN caching for global content distribution
- Application-level caching for frequently accessed data
- Database query caching for improved response times
Monitoring and Analytics: Backend systems likely include comprehensive monitoring for:
- Application performance metrics
- User behavior analytics
- Error tracking and debugging
- Security monitoring and threat detection
Security Implementation: Modern web security requires multiple layers:
- HTTPS encryption for all communications
- Content Security Policy headers
- Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) management
- Input validation and sanitization
- DDoS protection and rate limiting
Database Architecture
While QR generation occurs client-side, the platform requires database systems for various functions:
Analytics Database: Stores usage statistics, performance metrics, and user behavior data. This information helps optimize the service and understand usage patterns.
Configuration Storage: Maintains application settings, feature flags, and deployment configurations. This system enables dynamic service management without code deployments.
Logging System: Captures application logs, error reports, and security events for monitoring and debugging purposes.
Color Customization and Visual Design
Color Theory in QR Code Design
The Online-Tools.io generator’s color customization features require careful consideration of readability and scannability factors.
Contrast Requirements: QR code scanners rely on contrast between foreground and background elements to identify patterns. The generator must ensure sufficient contrast regardless of user color selections.
Color Space Management: The tool handles color input in various formats including hex codes, RGB values, and HSL representations. Internal color processing maintains accuracy across different display devices and printing systems.
Accessibility Considerations: Color choices must consider visual accessibility requirements, ensuring QR codes remain functional for users with color vision differences.
Advanced Visual Features
Transparency Support: The ability to generate QR codes with transparent backgrounds enables integration into diverse design contexts. This feature requires sophisticated image processing to maintain edge quality and scanner compatibility.
Brand Integration: Color customization enables brand alignment by allowing corporate colors in QR codes. This feature supports marketing applications while maintaining functional scanning capabilities.
Print Optimization: The generator produces output optimized for both digital display and print applications. This dual-purpose design ensures consistent appearance across different media.
Performance Optimization and Scalability
Client-Side Performance
Real-Time Generation: The immediate QR code generation upon input change requires efficient client-side algorithms. The implementation must balance generation speed with code quality and accuracy.
Memory Management: Client-side QR generation involves significant computation and memory usage. The system must manage resources efficiently to prevent browser performance degradation.
Progressive Enhancement: The application maintains functionality across different browser capabilities, ensuring accessibility even on older devices with limited JavaScript support.
Server-Side Scalability
Horizontal Scaling: The architecture supports scaling across multiple server instances to handle increased traffic loads. This approach enables global deployment and high availability.
Resource Optimization: Server resources are optimized for the specific requirements of a QR generation service, minimizing computational overhead while maximizing throughput.
CDN Integration: Content delivery networks reduce server load by distributing static assets globally, improving performance for international users.
Security Considerations and Privacy Protection
Data Privacy
No Data Storage: The tool’s design philosophy emphasizes user privacy by not storing input data on servers. All processing occurs client-side, ensuring sensitive information remains on the user’s device.
Anonymous Usage: The service operates without requiring user registration or personal information, maintaining anonymity while providing full functionality.
HTTPS Encryption: All communications between users and servers are encrypted, protecting data in transit even though processing occurs client-side.
Security Measures
Input Validation: The system validates all user input to prevent malicious code injection or system exploitation attempts.
Rate Limiting: Backend systems likely implement rate limiting to prevent abuse and ensure fair resource allocation among users.
Content Security Policy: Modern web security headers protect against various attack vectors including cross-site scripting (XSS) and clickjacking attempts.
Practical Applications and Use Cases
Business Applications
Marketing and Advertising: QR codes provide seamless bridges between physical and digital marketing materials. Businesses use them on print advertisements, product packaging, and promotional materials to direct customers to websites, special offers, or social media pages.
Contact Information Sharing: Business cards incorporating QR codes enable instant contact information transfer to smartphones. The vCard format encoding allows comprehensive contact data including names, phone numbers, email addresses, and company information.
Event Management: Conferences, concerts, and other events use QR codes for ticket validation, attendee registration, and information distribution. The codes can link to event schedules, speaker information, or feedback forms.
Payment Processing: Many payment systems utilize QR codes for transaction initiation, enabling customers to scan codes with mobile payment applications for instant payment processing.
Educational Applications
Resource Sharing: Educational institutions use QR codes to provide students with quick access to supplementary materials, online resources, and assignment submissions.
Interactive Learning: QR codes can link to videos, interactive exercises, or additional information that enhances traditional learning materials.
Administrative Efficiency: Schools use QR codes for attendance tracking, library book management, and campus navigation assistance.
Personal Applications
WiFi Sharing: QR codes can encode WiFi network credentials, allowing guests to connect to networks without manually entering complex passwords.
Social Media Integration: Personal QR codes can link to social media profiles, enabling quick connections and follower growth.
Event Coordination: Personal event invitations and coordination benefit from QR codes linking to calendar entries, location information, and RSVP systems.
Comparison with Alternative Solutions
Market Position Analysis
The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator competes in a crowded market with numerous alternatives, each offering different features and pricing models.
Free vs. Premium Services: While many QR generators offer basic functionality for free, premium services provide advanced features such as dynamic codes, analytics, and custom branding. The Online-Tools.io solution positions itself in the free tier with enhanced customization options.
Feature Comparison: Key differentiating factors include:
- Color customization capabilities
- Output format options
- Generation speed and reliability
- User interface design and ease of use
- Privacy and data handling policies
Technical Advantages: The client-side generation approach offers several advantages:
- Faster response times due to no server processing delays
- Enhanced privacy through local data processing
- Reduced server infrastructure costs
- Improved scalability through distributed processing
Competitive Analysis
Google QR Code Generator: Google’s solution integrates with other Google services but offers limited customization options.
QR-Code-Generator.com: Provides comprehensive QR code solutions including dynamic codes and analytics, but requires registration for advanced features.
Adobe QR Code Generator: Integrates with Creative Cloud applications but focuses primarily on design workflow integration rather than standalone generation.
Smartphone Native Solutions: Many smartphones include built-in QR code generation, but typically with minimal customization options.
Technical Deep Dive: QR Code Structure
Physical Structure Components
Understanding the physical structure of QR codes illuminates the technical challenges addressed by generators like Online-Tools.io.
Finder Patterns: Three large squares positioned at three corners of the QR code enable scanners to identify and orient the code correctly. These patterns use a specific 1:1:3:1:1 ratio that remains recognizable across various sizes and orientations.
Separator Patterns: White borders surrounding finder patterns ensure proper pattern recognition by providing contrast separation from data areas.
Timing Patterns: Alternating black and white modules connecting finder patterns enable scanners to determine module size and coordinate systems within the code.
Alignment Patterns: Larger QR codes include additional alignment patterns to maintain geometric accuracy across the entire code area.
Format Information: Critical metadata including error correction level and masking pattern information are encoded in specific locations adjacent to finder patterns.
Version Information: QR codes version 7 and higher include version information encoded in two locations to ensure proper decoding configuration.
Data and Error Correction Areas: The remaining space contains actual data interspersed with error correction codes following specific interleaving patterns.
Masking and Pattern Optimization
QR codes implement masking patterns to optimize readability and prevent problematic patterns that might interfere with scanning.
Masking Patterns: Eight different masking patterns are available, each designed to address specific scanning challenges such as large areas of uniform color or patterns that might be confused with finder patterns.
Pattern Selection: Generators evaluate all eight masking options and select the pattern that produces the best balance of visual distribution and scanning reliability.
Penalty Scoring: A sophisticated scoring system evaluates pattern quality based on factors such as:
- Adjacent module similarity
- Block pattern detection
- Ratio pattern identification
- Dark module balance
Advanced Implementation Techniques
Optimization Algorithms
Modern QR code generators like Online-Tools.io implement sophisticated optimization techniques to produce high-quality codes efficiently.
Data Segmentation: Advanced generators analyze input data to identify optimal segmentation points for mixed-mode encoding, potentially reducing overall code size.
Error Correction Optimization: Dynamic error correction level selection based on intended use case and environmental factors ensures optimal balance between data capacity and reliability.
Version Minimization: Sophisticated algorithms determine the smallest QR code version capable of containing the required data, minimizing physical size while maintaining readability.
Quality Assurance
Verification Algorithms: Generated QR codes undergo automatic verification to ensure scannability before presentation to users.
Cross-Platform Testing: Quality systems verify QR code compatibility across different scanning devices and applications.
Print Quality Optimization: Output optimization ensures consistent appearance between digital display and various printing systems.
Integration Capabilities and API Potential
Programmatic Access
While the Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator primarily serves as a web-based tool, similar systems often provide API access for developers.
REST API Architecture: Modern QR generation services typically offer RESTful APIs enabling programmatic QR code generation with standard HTTP requests.
Authentication and Rate Limiting: API access requires robust authentication systems and rate limiting to prevent abuse while ensuring legitimate usage.
Response Formats: APIs typically support multiple output formats including base64-encoded images, direct image responses, and SVG vector formats.
Third-Party Integrations
Content Management Systems: QR generators can integrate with popular CMS platforms through plugins and extensions.
E-commerce Platforms: Integration with online stores enables automatic QR code generation for products, orders, and customer communications.
Marketing Automation: CRM and marketing platforms benefit from QR code generation capabilities for campaign management and customer engagement.
Mobile Responsiveness and Cross-Platform Compatibility
Responsive Design Implementation
The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator must function effectively across diverse device types and screen sizes.
Flexible Layouts: CSS Grid and Flexbox technologies enable layouts that adapt to various screen dimensions while maintaining usability.
Touch Interface Optimization: Mobile interfaces require larger touch targets, simplified navigation, and gesture-friendly interactions.
Performance Considerations: Mobile devices have computational limitations that require optimized JavaScript execution and memory management.
Cross-Browser Compatibility
Progressive Enhancement: The application maintains core functionality across browsers with varying JavaScript capabilities.
Polyfill Implementation: Modern web APIs may require polyfills for older browser support, ensuring consistent functionality across different environments.
Testing Protocols: Comprehensive testing across browser versions and device types ensures reliable operation for all users.
Analytics and Usage Monitoring
Performance Metrics
Successful web applications require comprehensive monitoring and analytics systems to understand usage patterns and optimize performance.
User Engagement Metrics: Analytics track user interaction patterns, session duration, and feature utilization to guide development priorities.
Performance Monitoring: Response times, error rates, and resource utilization provide insights into system health and optimization opportunities.
Conversion Tracking: Understanding how users progress through the QR generation process identifies potential improvements and pain points.
Data-Driven Optimization
A/B Testing: Interface modifications and feature changes benefit from controlled testing to measure impact on user satisfaction and engagement.
Usage Pattern Analysis: Understanding common use cases and data types enables targeted optimizations and feature development.
Geographic Distribution: Global usage patterns inform CDN optimization and localization priorities.
Future Enhancements and Technology Evolution
Emerging Technologies
The QR code generation landscape continues evolving with new technologies and capabilities.
Machine Learning Integration: AI algorithms can optimize QR code generation based on usage patterns, error rates, and scanning success metrics.
Advanced Graphics: Future implementations may support more sophisticated visual customization including gradients, patterns, and embedded graphics while maintaining scannability.
Dynamic Content: Integration with content management systems enables QR codes that automatically update their target destinations without regeneration.
Standards Evolution
Enhanced Specifications: QR code standards continue evolving with new versions supporting increased data capacity and improved error correction.
Security Enhancements: Future QR code implementations may include cryptographic signatures or validation mechanisms to prevent malicious code injection.
Accessibility Improvements: Ongoing development focuses on improving accessibility for users with visual impairments and various assistive technologies.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Digital Efficiency
Modern web applications like the Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator must consider environmental impact and sustainability factors.
Energy Efficiency: Client-side processing reduces server energy consumption by distributing computational load to user devices.
Bandwidth Optimization: Efficient code delivery and minimal resource requirements reduce network energy consumption and improve accessibility for users with limited connectivity.
Longevity Design: Creating QR codes that remain functional over extended periods reduces the need for regeneration and associated resource consumption.
Sustainable Practices
Code Reusability: Permanent QR codes reduce the need for frequent regeneration, supporting sustainable usage patterns.
Print Optimization: High-quality output reduces printing waste from failed scans and reprints.
Digital-First Approach: Web-based tools reduce the environmental impact compared to desktop software requiring installation and updates.
Advanced Functionality
The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator represents a sophisticated implementation of QR code technology that successfully balances advanced functionality with user-friendly design. Through its combination of real-time generation, color customization, privacy protection, and professional-grade output quality, the tool addresses diverse user needs while maintaining technical excellence.
The service’s architecture demonstrates modern web development best practices, employing client-side processing for enhanced privacy and performance while maintaining robust backend infrastructure for global accessibility and reliability. The implementation of Reed-Solomon error correction, advanced encoding optimizations, and comprehensive quality assurance ensures that generated QR codes meet professional standards for both digital and print applications.
From a technical perspective, the tool showcases the evolution of web-based utilities from simple form-processing applications to sophisticated, real-time processing systems. The integration of advanced features such as transparent background support, comprehensive color customization, and instant generation reflects the maturation of web technologies and user expectations.
The practical applications of this tool extend far beyond simple URL encoding, supporting business marketing, educational resource sharing, event management, and personal communication enhancement. The tool’s accessibility without registration requirements and its commitment to user privacy make it particularly valuable in an era of increasing data protection awareness.
Looking forward, the Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator is well-positioned to evolve with emerging technologies and changing user needs. Its foundation in modern web technologies and adherence to established QR code standards provide a solid base for future enhancements while maintaining compatibility with existing systems and devices.
For businesses, educators, developers, and individuals seeking a reliable, feature-rich QR code generation solution, the Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator offers an optimal combination of functionality, performance, and accessibility that meets professional requirements while remaining approachable for casual users. Its technical sophistication, combined with thoughtful user experience design, establishes it as a valuable tool in the modern digital toolkit.
The continued importance of QR codes in bridging physical and digital experiences ensures that tools like this will remain relevant and valuable as our world becomes increasingly interconnected. The Online-Tools.io QR Code Generator’s comprehensive feature set and technical excellence position it as a leading solution in this essential technology category.